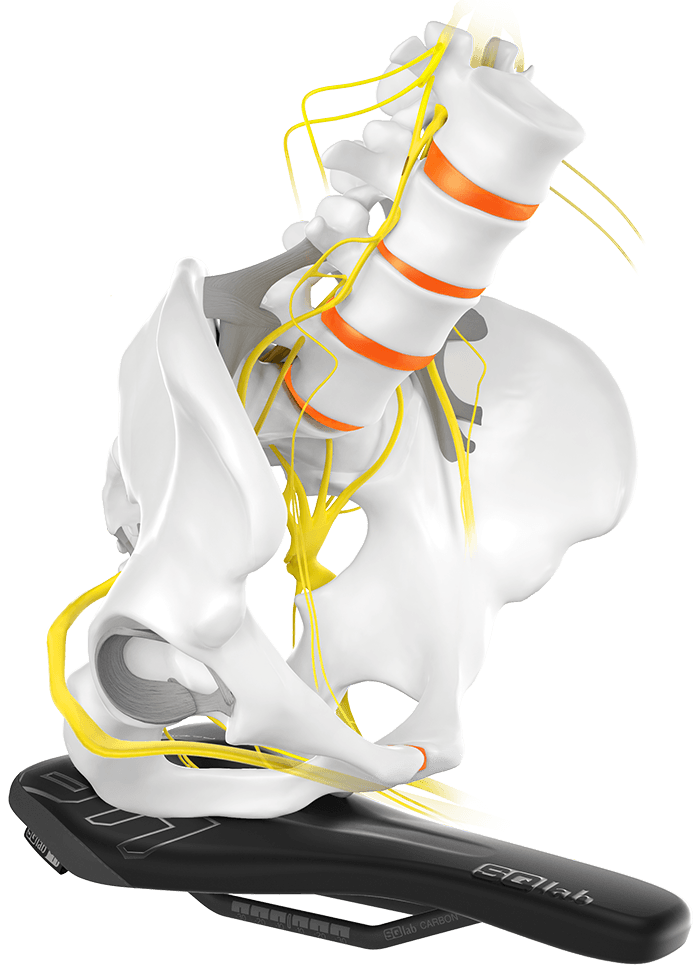
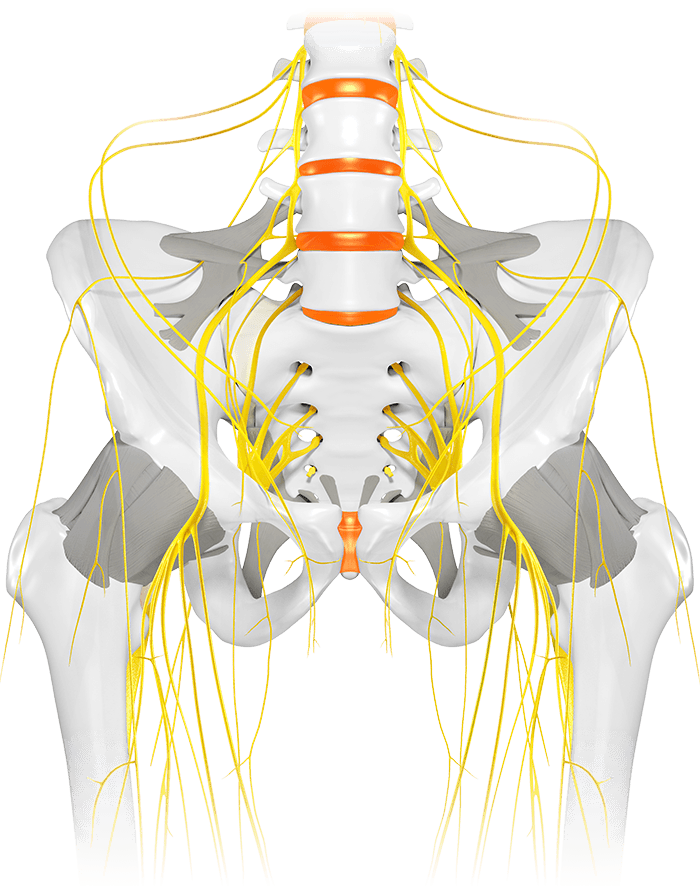
The saddle nose, which is lower in level, relieves the sensitive areas of both men and women. The differences in anatomy are covered by the different widths.
erectile Dysfunction and Impotence Study
Erectile dysfunction and impotence during cycling
At SQlab, we don't want to play on fear, we want to solve problems. Nevertheless, first of all we have to ask science and doctors how big and serious the problem is in cycling and its causes, so that we don't solve problems that don't exist at all.
There is no doubt about the issue of cycling and impotence. Impotent means infertility and erectile dysfunction. When erection is no longer adequate, we are talking about sexual performance or erectile dysfunction.
The latter diminishes with age. Alcohol, cigarettes with certainty lung impairment, lack of exercise, obesity and much more also affect this performance. It's not an "on / off" thing, it rises and falls. Like endurance performance in cycling, one person wins the marathon, the other is in the middle of the pack, but most are too unfit and give up on the first climb after the halfway point.
Sexual performance is actually directly related to endurance performance. In this respect, cycling, swimming, running is a perfect workout. Especially cycling is a long lasting endurance performance. On top of that it is directly coming out of the pelvis - perfect. Unfortunately, studies show that the number of men suffering from erectile dysfunction is up to 4 times higher among cyclists than among runners or swimmers. This can be clearly attributed to the saddle. Especially since there have been many studies on this subject. Between 1995 and 2004 in particular, with clear results that illustrate the negative effects of incorrect saddle shapes: of 34 studies, 33 have concluded that there is a relatively large, often underestimated risk that cycling increases the "erectile dysfunction" risk. Nevertheless, cycling is recommended. It is only important not to disregard the alarm sign "numbness" and to pay attention to the correct saddle width as well as a deeper saddle nose.
As a result, we at SQlab have developed the saddle width system and the step saddle concept to successfully solve the aforementioned problems. With a new study in 2021 by Masterand Lukas Fritsch on the subject of "Perineal stress while cycling", SQlab has once again reviewed the studies of the past with the technologies of today and compared current saddle concepts with each other.
"Perineal stress during cycling"
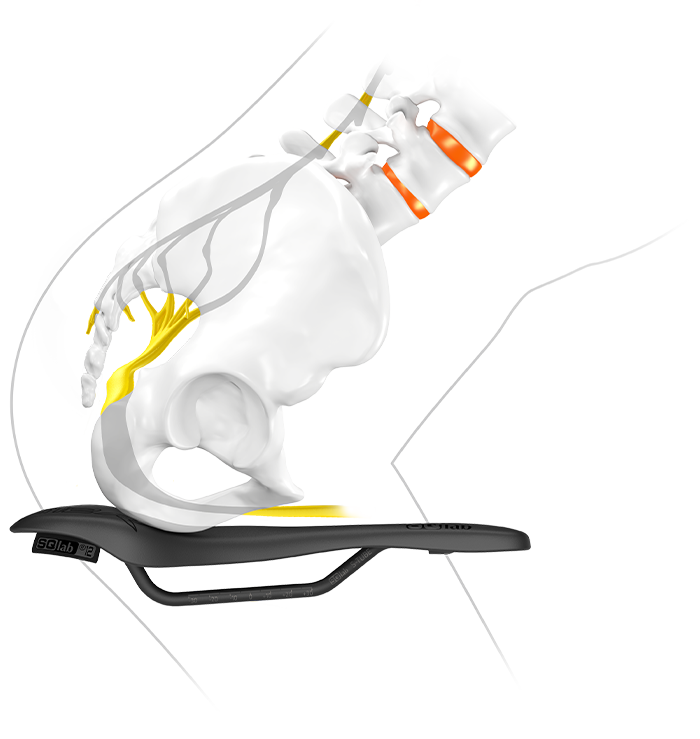
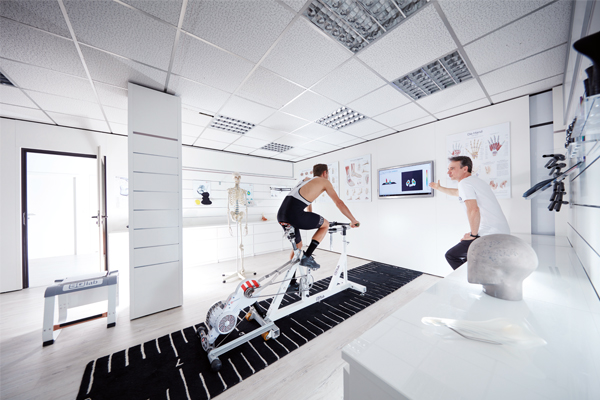
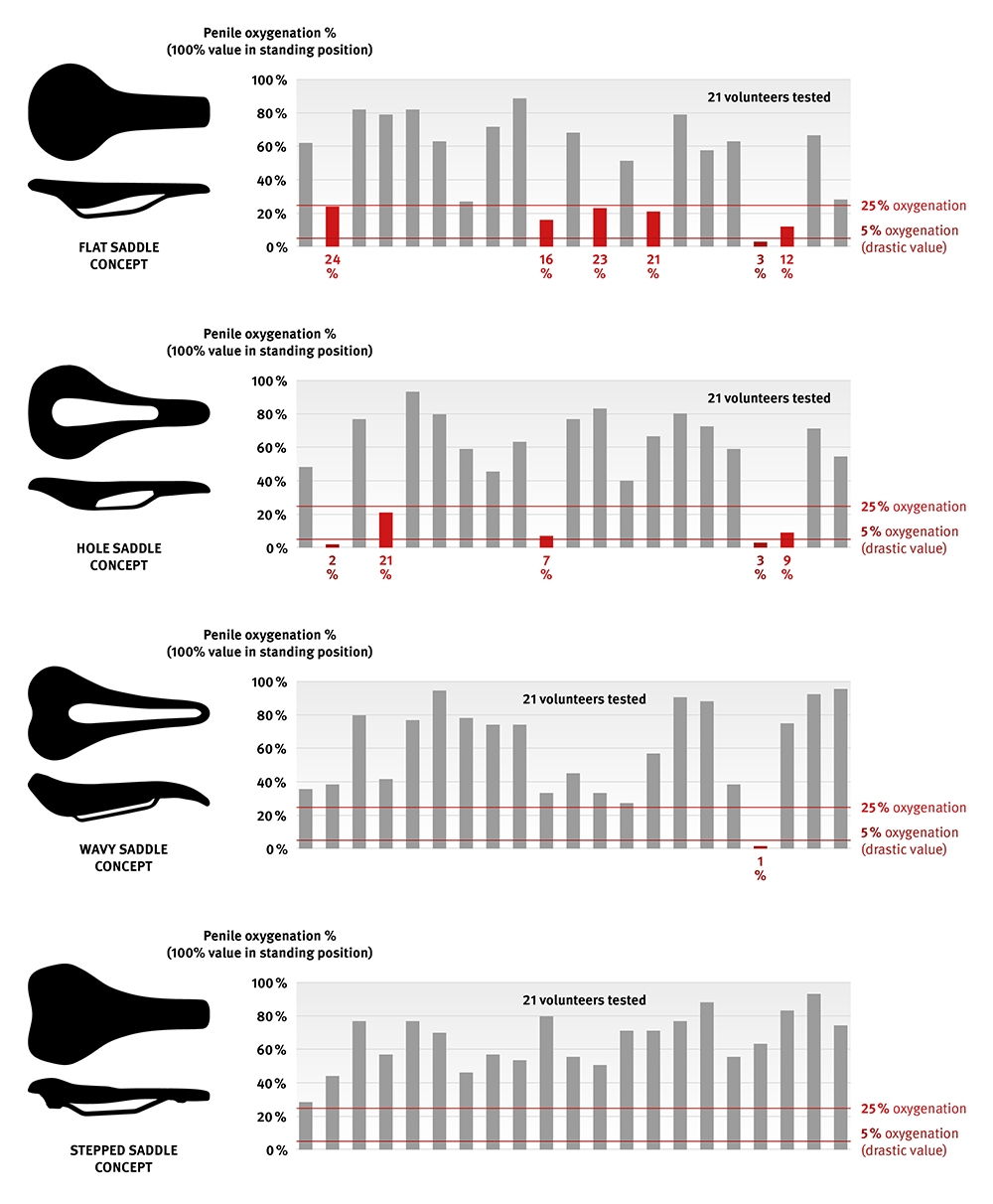
In sporty cycling, the main load support is on the saddle. This load often occurs in the perineal area. However, the basic shape of a saddle concept should aim to minimize perineal load. To examine the perineal load, a master's thesis at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology compared the influence of the following bicycle saddle concepts: flat (FK), hole (LK), wavy (GK) and the stepped saddle concept (SK). Perineal stress was evaluated by transcutaneous oxygen partial pressure, dynamic pressure measurement analysis and subjective comfort.
Results "Oxygenation of the Penis“
For the analysis, 21 male volunteers rode four different saddle concepts on a stationary cycle ergometer with an upper body angle of 40° to the horizontal in a randomized testing session. Oxygen supply to the glans penis, mean and maximum pressure (medilogic pressure measurement film), and subjective comfort were recorded. The results show on the basis of individuality, that the perineal load is strongly dependent on the person.
"One in three volunteers is below 25% oxygenation with flat saddle concept."
In addition, for the flat saddle concept, for the hole saddle and for the wavy saddle, volunteers are found below critical 5% of penile oxygenation. This phenomenon does not occur with the step saddle concept.
What happens when the oxygen supply is too low?
Too low oxygen supply provokes the development of conjunctive tissue and leads to a kind of "calcification" / narrowing of the arteries. This reduces the required blood flow, which in advanced stages leads to erectile dysfunction. This effect can already be observed with only 25% oxygen supply. In the short term (a few minutes) this is within the tolerance, but in the long term, for example over the duration of a cycling tour, it is important not to drop below this 25% level. The value should not drop below 5% of the oxygen supply in any situation, as this can lead directly to mortify of tissue.
"Pressure Measurement & Comfort"
Furthermore, in comparison to the other concepts, fewer pressure peaks above 15 N/cm2 (maximum tissue tolerance (Staudte, 2013/2016)) were noted with the "Stepped" saddle. The "Flat" concept causes pressure values above this limit in the perineal area in 9 probands, the "Hole" concept in 13 probands, and the " Waved" and "Stepped" concepts in 7 probands each. Thus, especially with the "Flat" and "Hole" concepts, approx. 40-59% of the sample are exposed to damaging pressure peaks in the area of the sensitive structures of the perineal area. Moreover, the maxima of these pressure peaks are higher than those of the "Stepped" concept (LK: 38 N/cm2, SK 22N/cm2). In addition, the "Stepped" concept exhibits the lowest discomfort in the subjective evaluation of perineal stress compared to the other saddle concepts.
Conclusion of the study
In general, when analyzing perineal loads during cycling, there is a large intra- and inter-individuality to consider. In this regard, the load can strongly depend on the individual anatomy as well as the 3D pelvic motion.
However, it is evident that in terms of perineal blood flow, the stepped saddle concept has advantages.
Important for the perineal relief is therefore primarily the appropriate saddle width oriented to the purpose and the sitting position as well as the step saddle shape.
Study situation to date
Scientific studies have shown that athletes generally suffer from erectile dysfunction (e.D.) less frequently than non-athletes. Results from several studies indicate that approximately 6-10% of all men between 30 and 50 years of age suffer from moderate to severe e.D. A very significant study among athletes showed that 1.1% of runners suffer from moderate to severe e.D., 2% of swimmers and 4.2% among cyclists. Assuming that the positive effects of cycling are at least comparable to those of running, for 3.1% of cyclists, instead of an improvement, there is a decrease up to the critical range. But it doesn't always have to come to the worst - sexual performance rises and falls just like muscle strength or endurance performance, for example. With increasing age, however, it decreases disproportionately. So it makes sense to do sports, especially cycling, but to pay attention to the anatomically correct saddle. It would be a pity if the positive effects were negated by the wrong saddle.
In 2001, a study was published by Dr. Frank Sommer, who measured the oxygen supply to the penis during cycling. With the result that after only 10 minutes the value drops to an alarming level, where temporary restrictions of sexual performance are to be expected in any case. Already then different saddle forms were tested: Hole saddle, wavy saddle and flat, soft saddle. The result was that all three saddle designs showed similarly poor values. The (then) modern saddles with hole or V-cut, i.e. the supposed solution, showed worse values than the classic problem saddle. The only saddle with good values was the classic Rocksaddle, an oval board from the Netherlands.
In 2003, a study on the same subject was published with the result of pressure measurement tests. It showed that hole saddles are harmful for both men and women because they concentrate the pressure on the edge zones of the hole.
Source Reference: (Huang V, Munarriz R, Goldstein I., Institute for Sexual Medicine, Department of Urology, Boston University School of Medicine, 720 Harrison Avenue, Boston, MA 02118, USA., Sep. 2005)








.contact)