Sit bone pain
Sit bone Pain while cyclingSit bone pain when cycling is a common problem that affects many cyclists. The main causes include a saddle that is too narrow or too soft and an unsuitable saddle shape that does not provide sufficient support. In addition, a lack of acclimatization to longer rides and shear forces generated by cycling can cause discomfort. Understanding these causes is crucial to finding targeted solutions and improving riding comfort. We have developed suitable solutions to remedy these problems, counteract them and enable pain-free cycling. |
Causes of painful sit bones
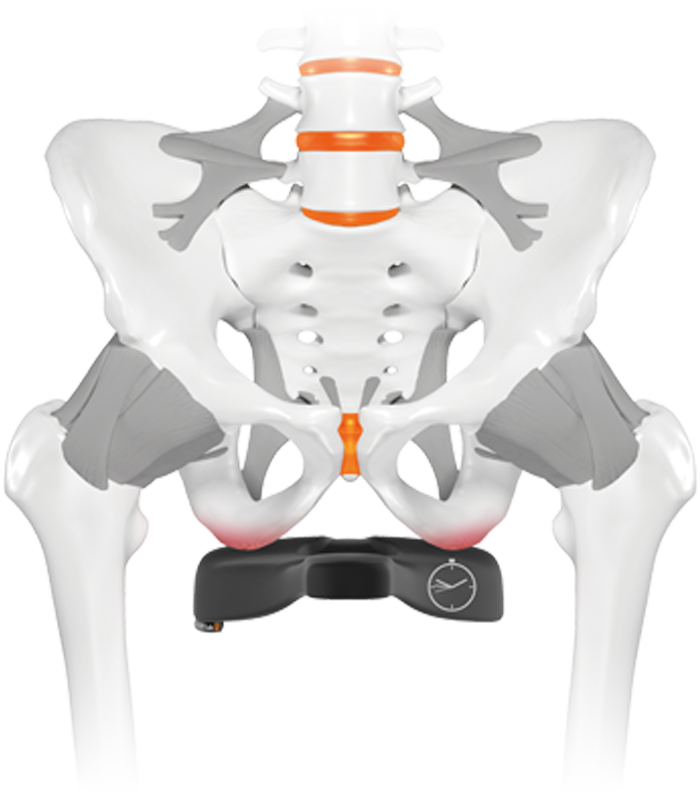
Saddle to narrow
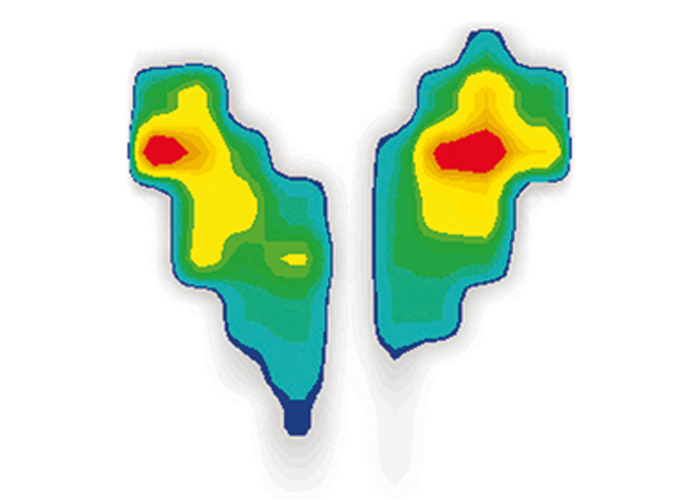
Saddle width
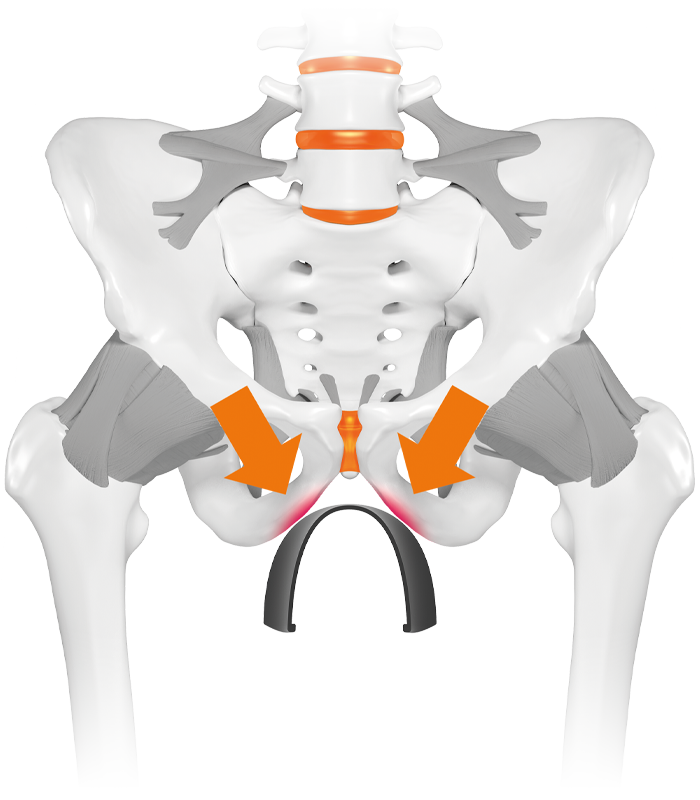
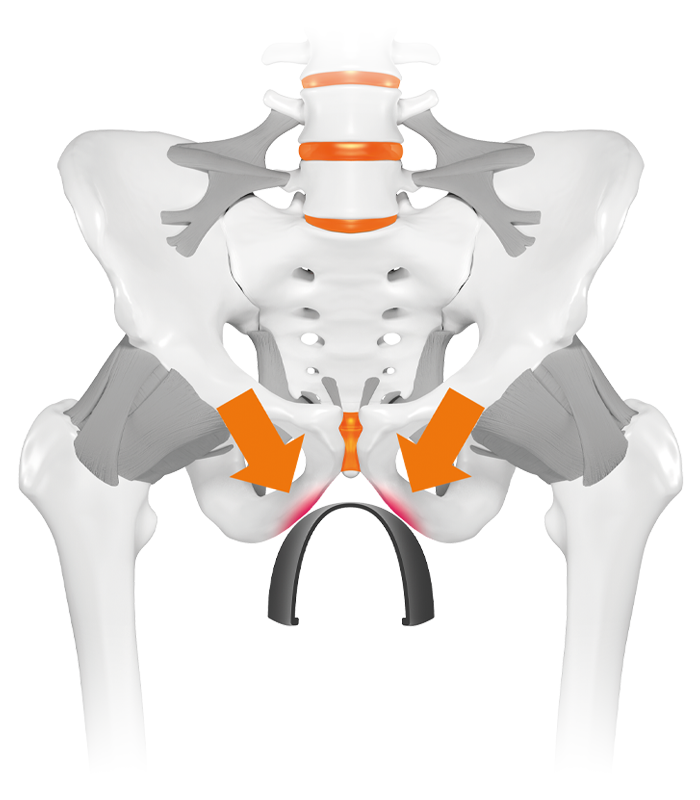
Wrong saddle shape
Cause - wrong saddle shape
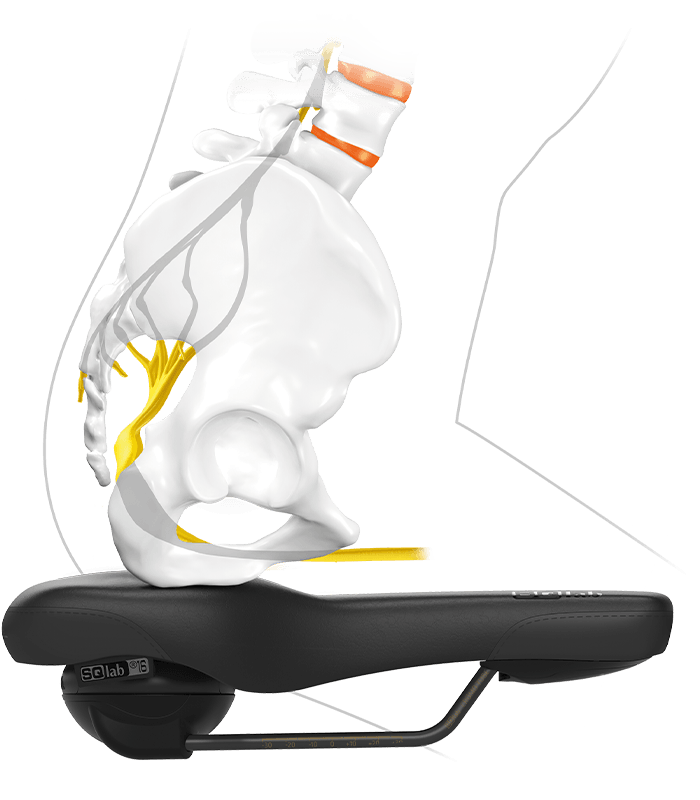
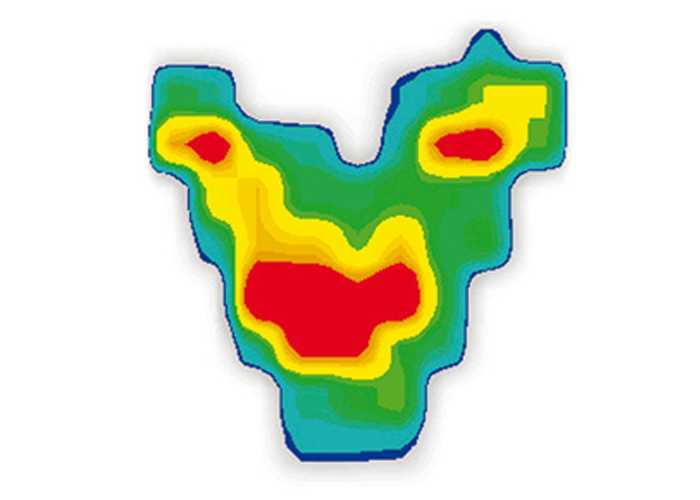
leads to an increased pressure in the perineal area
SQlab Solution
Step Saddle with an optimum pressure distribution in accordance with medical advice
Saddle Shape
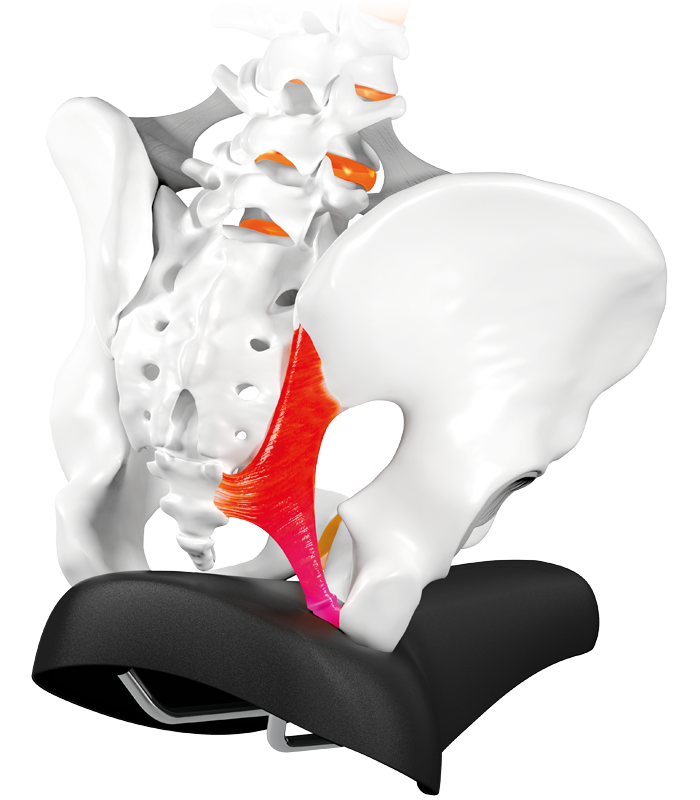
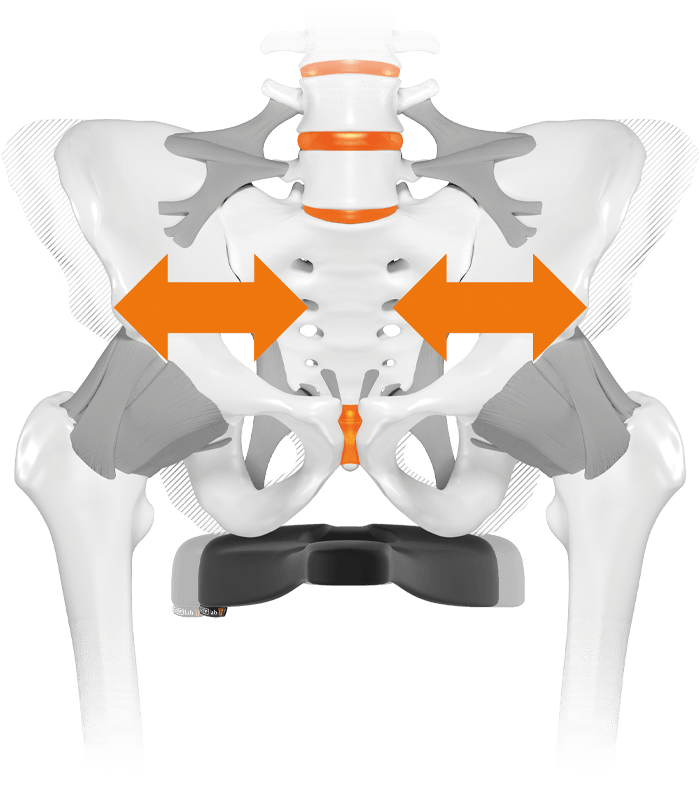
Too soft saddle
Cause - too soft saddle
leads to sinking sit bones
SQlab Solution
SQlab saddle models in different saddle firmnesses adapted to riding duration and area of use

The sit bones sink in so far, that sensitive soft tissue such as muscle and tendons are aggravated. After approx. 30 – 40 minutes a dull deep pressing pain sets in.
SQlab Solution Soft saddles are generally only suitable for short distances! |
Familiarization of the sit bones
The sit bones are capable of getting used to a high pressure load and the discomfort will reduce. At the beginning of the season, or when switching to a new unfamiliar saddle shape, pain and discomfort in the sit bones is normal. Familiarization with a new saddle can take approx. 5 to 6 rides.
At least two days of rest should be scheduled between the initial rides to give the already sensitive muscles and tendons time to respond.
SQlab lists the hardness of the padding material on the saddle. We have developed a measurement unit called SQ Shore, which takes into account the combination of both cover and padding materials.
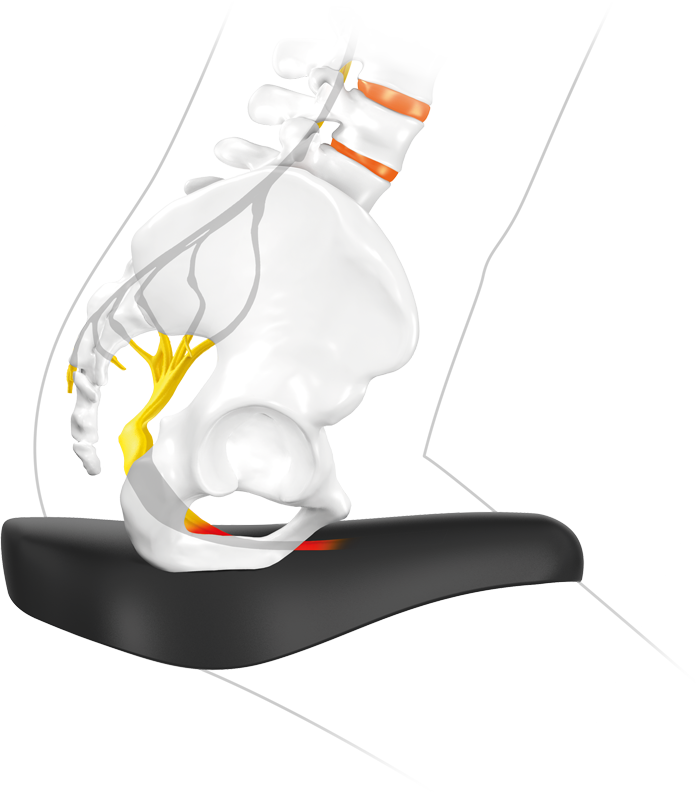
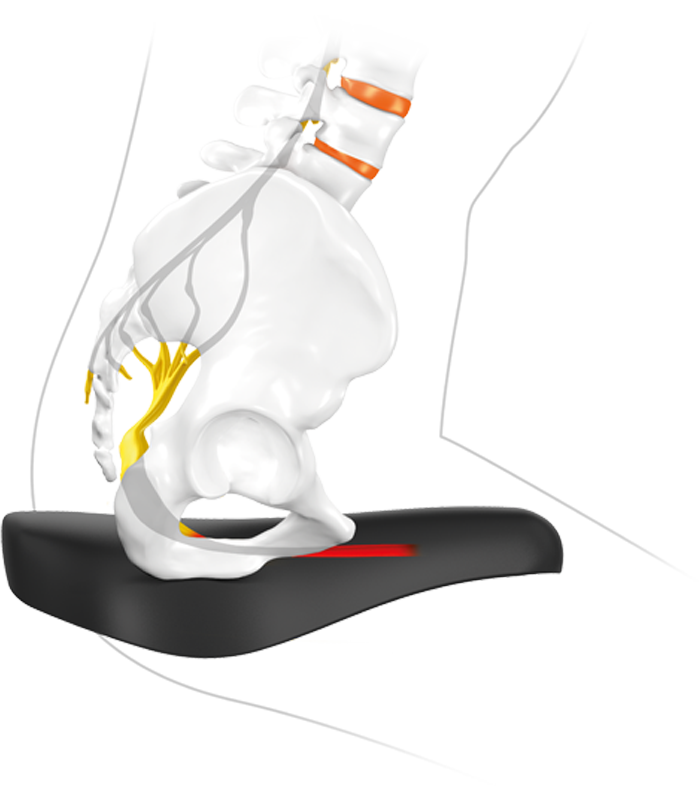
Shearing forces
Painful sit bones get used to the strain at first, which is quite normal especially in the spring after a long winter break or during the first test drives on the usually unfamiliar SQlab step saddle.
The pain originates at the periosteum. The pressure is less the problem, rather it is the shear forces caused by the pedaling motion. The slight but constant movement of the pelvis on the saddle provides painful shearing forces on the periosteum.
The SQlab active technology provides some relief as well as a chamois cream. The best solution are our new pads: The SQ-Pad 11 and SQ-Pad10. >More about SQ-Pad concept





.contact)