Knee pain
Knee pain while cycling?The causes of knee pain vary, but are usually related to the position on the bike and the position of the foot. If the foot or the pedal are not aligned correctly, this has a direct effect on the load on the knee joint. In addition to the correct adjustment of the cleats, SQlab insoles support the foot for optimal pressure distribution and better power transmission. We offer our pedals in different axle lengths for a natural foot position. |
CAUSES Knee pain while cycling
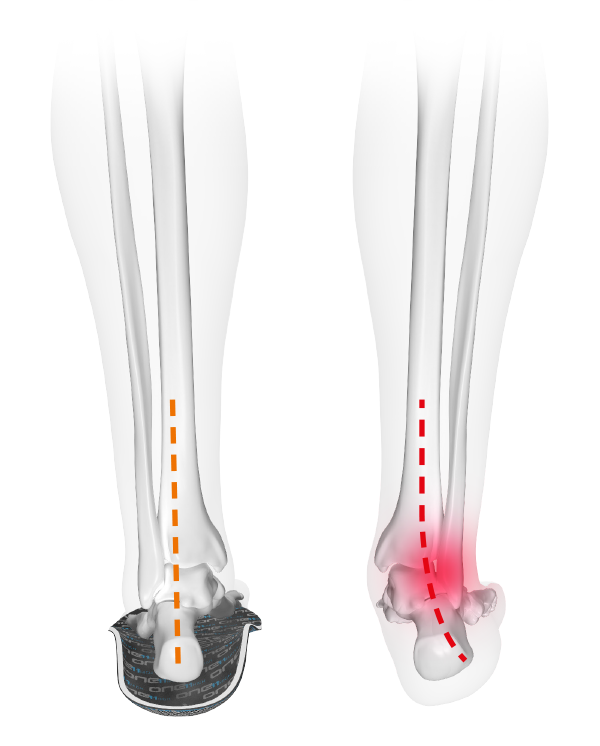
Knee pain - unnatural foot placement
CAUSE - one-sided load
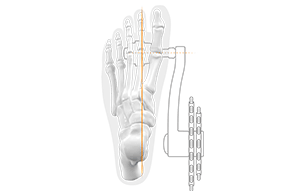
Pedals with a short axis usually allow only a parallel foot position
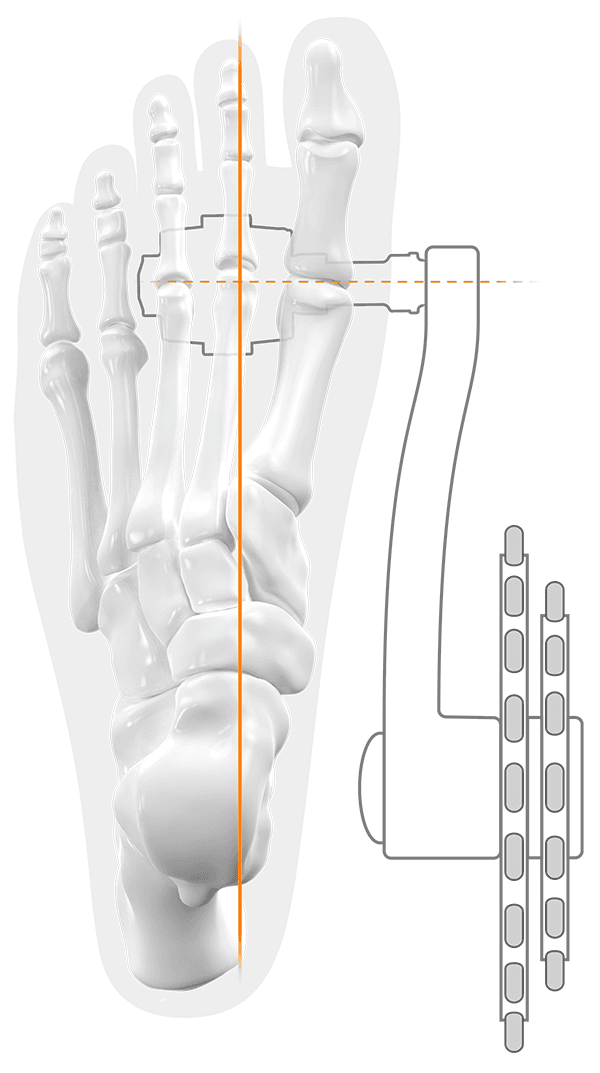
SQlab solution
different axle lengths for a natural foot position
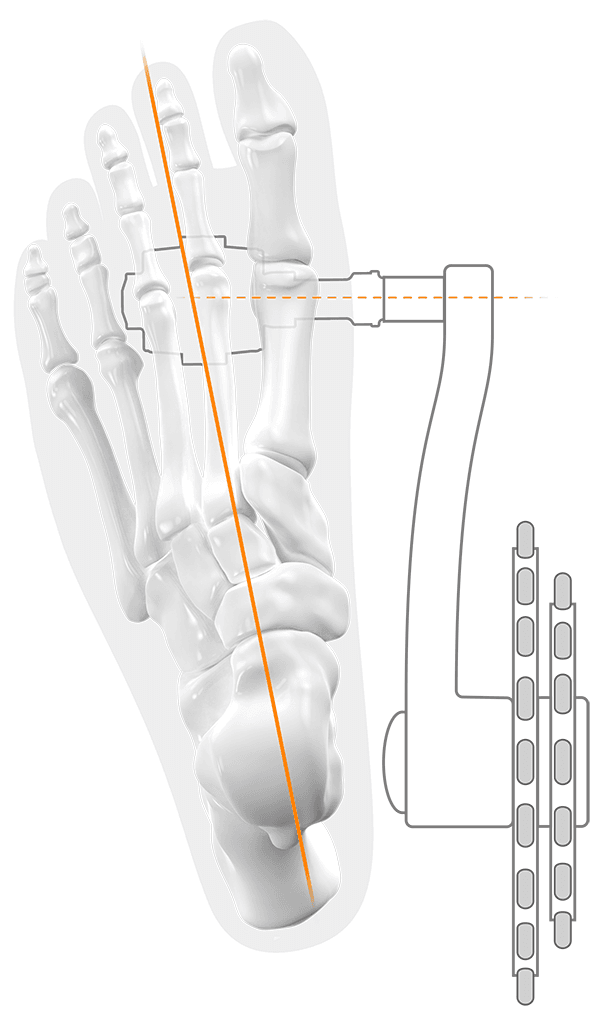
Conventional pedals force the feet into an almost parallel foot position. The extended axis of the SQlab pedals allows a physiological, more natural foot position. This prevents one-sided loading - especially in the case of fibula head syndrome.
Our pedals are available in up to four axle lengths.
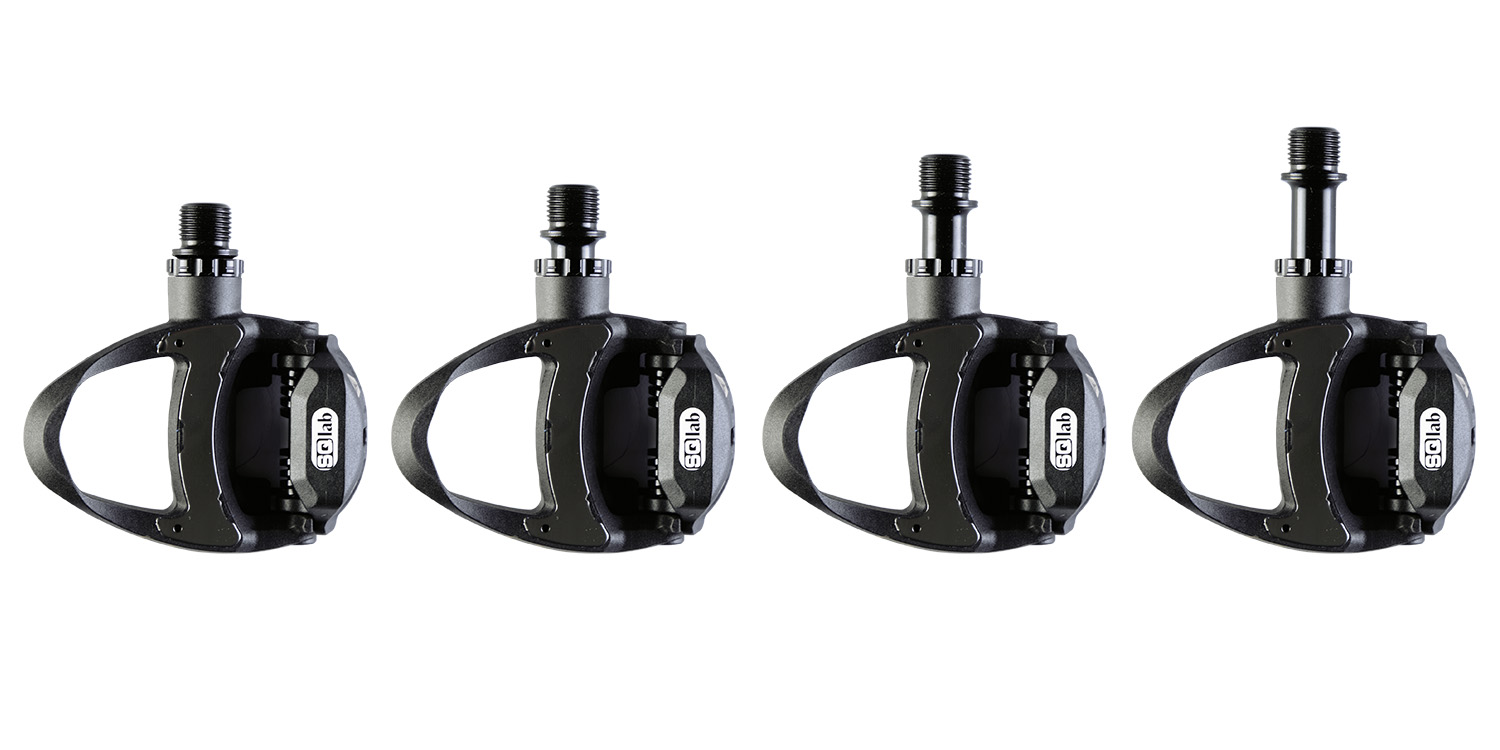

Shorter axle
These pedals are rarely needed but still have their place in our product line-up. These pedals can be used by cyclists with small shoe sizes that have a parallel foot position, herewith reducing the Q-factor. Especially in combination with a small sit bone distance and small hip width it makes a lot of sense to keep the feet as close as possible.
Middle sized axle
The standard dimensioned pedal axle for all cyclists, that in all fairness, can also ride with regular pedals as offered from the leading manufacturers of this product segment without any problems.
Longer axle
This is important for riders who’s natural foot position is “V” shaped when viewed from above. If the feet are placed parallel on the pedals, this no longer corresponds to the natural position of the feet and knee issues can be the result. If you are affected by such a problem, especially if pain is experienced on the outside of the knees at the fibula / fibula head, then your feet should be positioned on the pedals in a more natural position is replicated. Most clipless pedals allow sufficient repositioning of the cleats for adjustment to this improved position. Usually this results in the heels clipping the chainstays or rubbing on the cranks. The longer axle of the SQlab pedals will provide the additionally required space for the improved foot position.
The other case where the longer SQlab pedal axles are often a solution is with large shoe sizes, typically from about size 45 upwards where the heels often polish the cranks with standard pedals.
Movement
Throughout a pedal turn, the foot tends to make a slight rotation. Almost all clipless pedals allow this slight rotation of the foot. Out of this reason, regular platform pedals should not be too grippy even if slipping-off presents a slight risk. Pedals with a large platform area and extremely good grip through pins that dig deeply into the sole of your shoes can cause a twisting of your knees when riding but also when getting off your bike.
Plattform area
The platform area on the SQlab pedals is always horizontal. Humans have been used to walking on even ground for millions of years. Even if the pedaling motion is still very new to the biomechanical development of humans, the foot angle is still a very individual measurement. The positioning of the foot is best performed with the shoe on and with insoles in place.
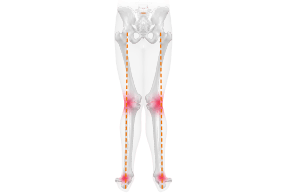
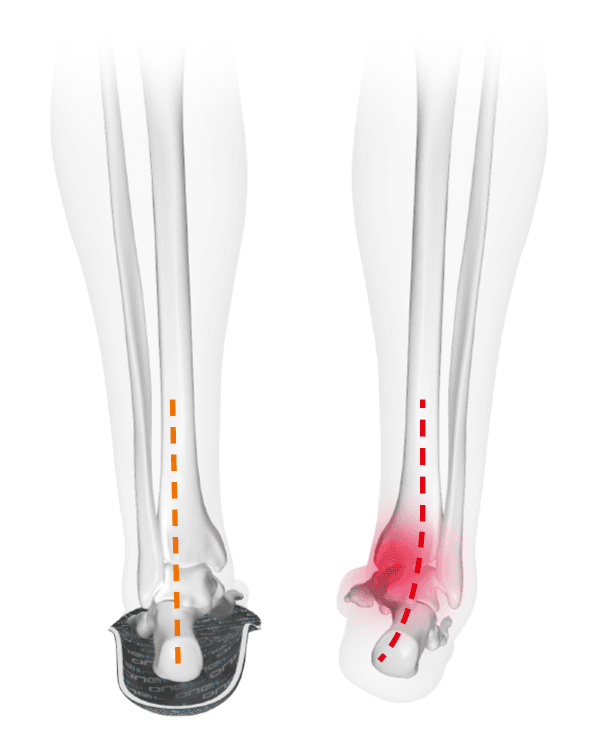
Knee pain - Malalignment of the leg axis
CAUSE - malposition in the knee
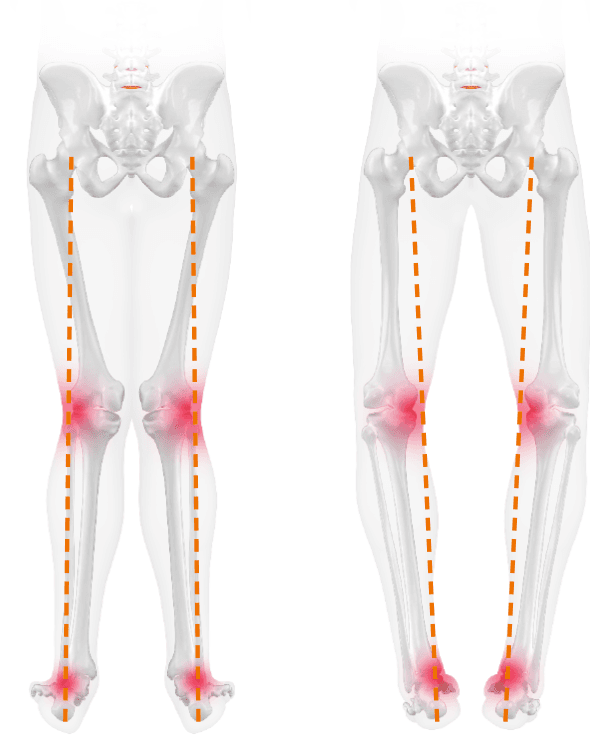
due to X- or O-legs
SQlab solution
insoles that support the respective weak point
Due to instability or muscular imbalances, the knee can move inward or outward from the leg axis while standing or pedaling (also called O-leg or X-leg). The resulting one-sided strain can cause knee pain.
Especially with more pronounced leg axes and foot arches, the musculature around the knee joint and ankle joint is strongly overstrained without support and is permanently brought into an unnatural position (knee tilts inward or outward).
Due to the resulting muscular tension and instability, the longitudinal arch is permanently overstrained and promotes knee pain. Depending on the foot type (based on the SQlab foot type determination), SQlab insoles support the arch of the foot to varying degrees in order to compensate for misalignments in the leg axes. This can reduce symptoms of fatigue and knee pain.
Therefore, it is clear that in addition to the foot type the leg axis is also important for the selection of the correct support level.
O-legs
Attention. Insoles do not make any orthopedic correction to the foot, but distribute the pressure optimally on the pedal. |
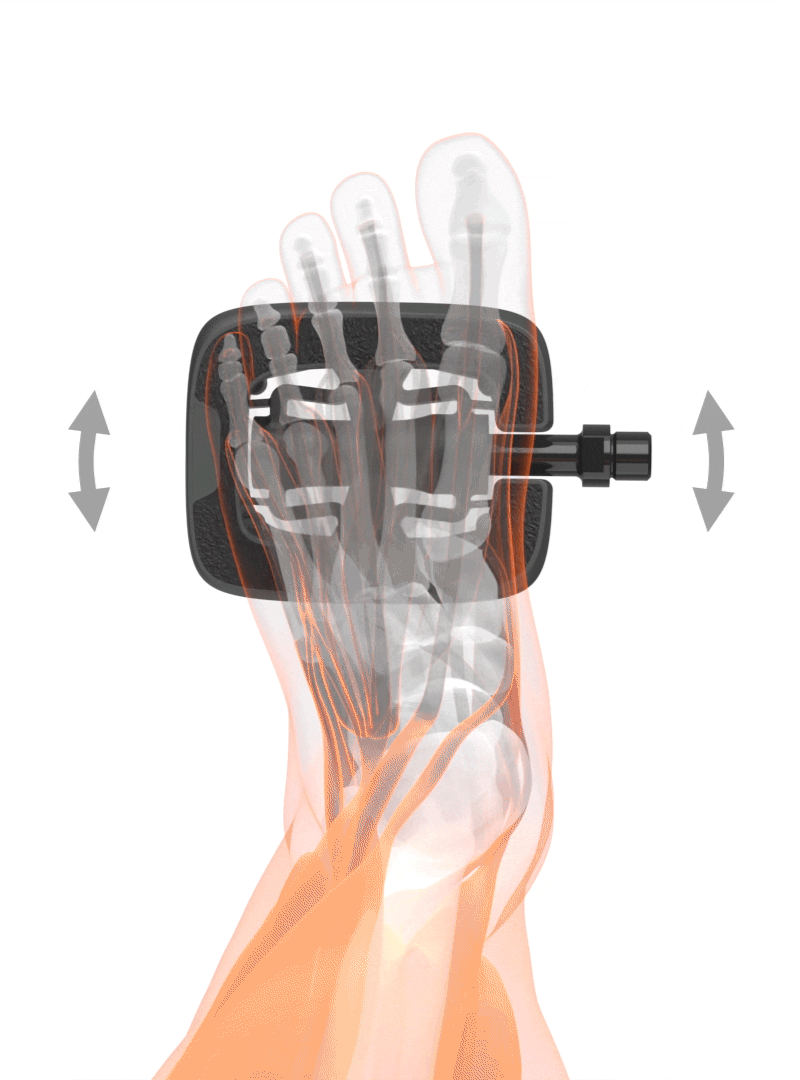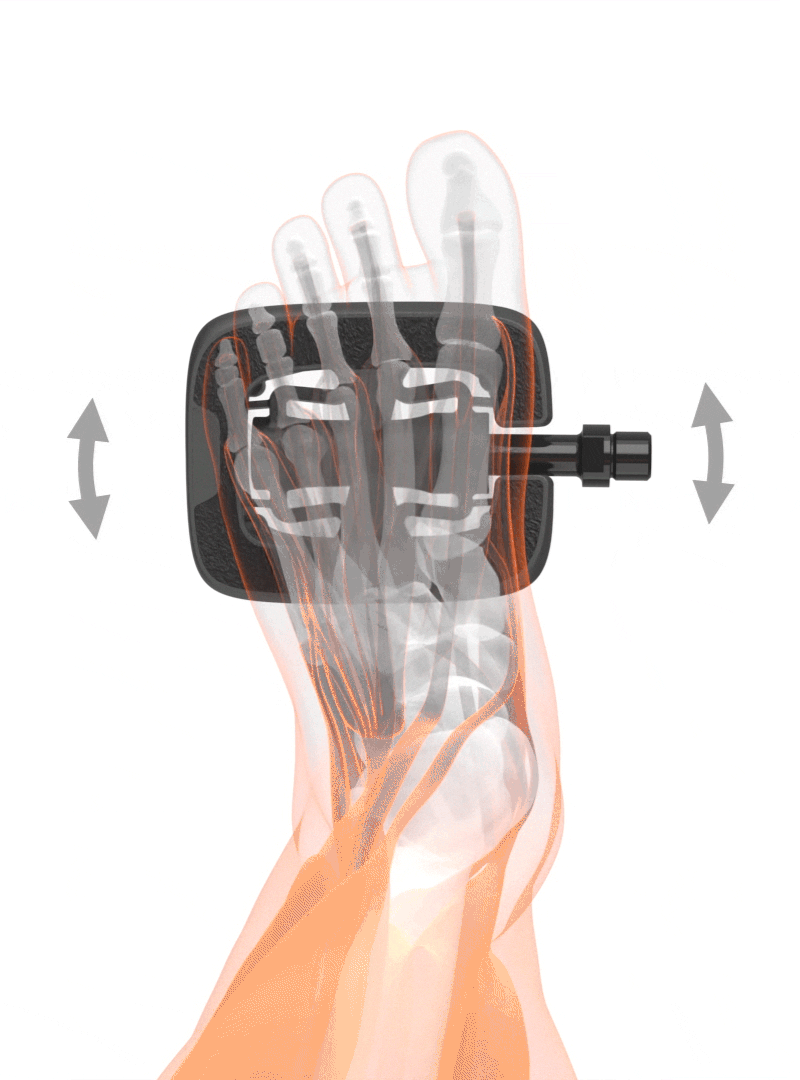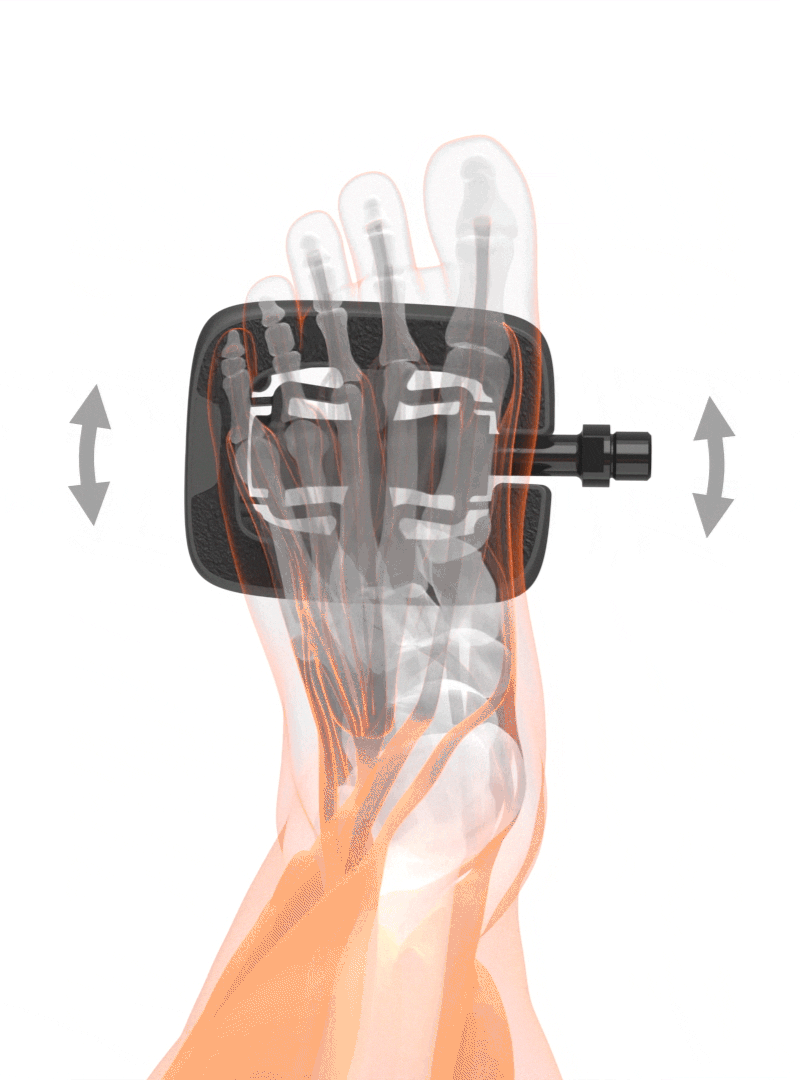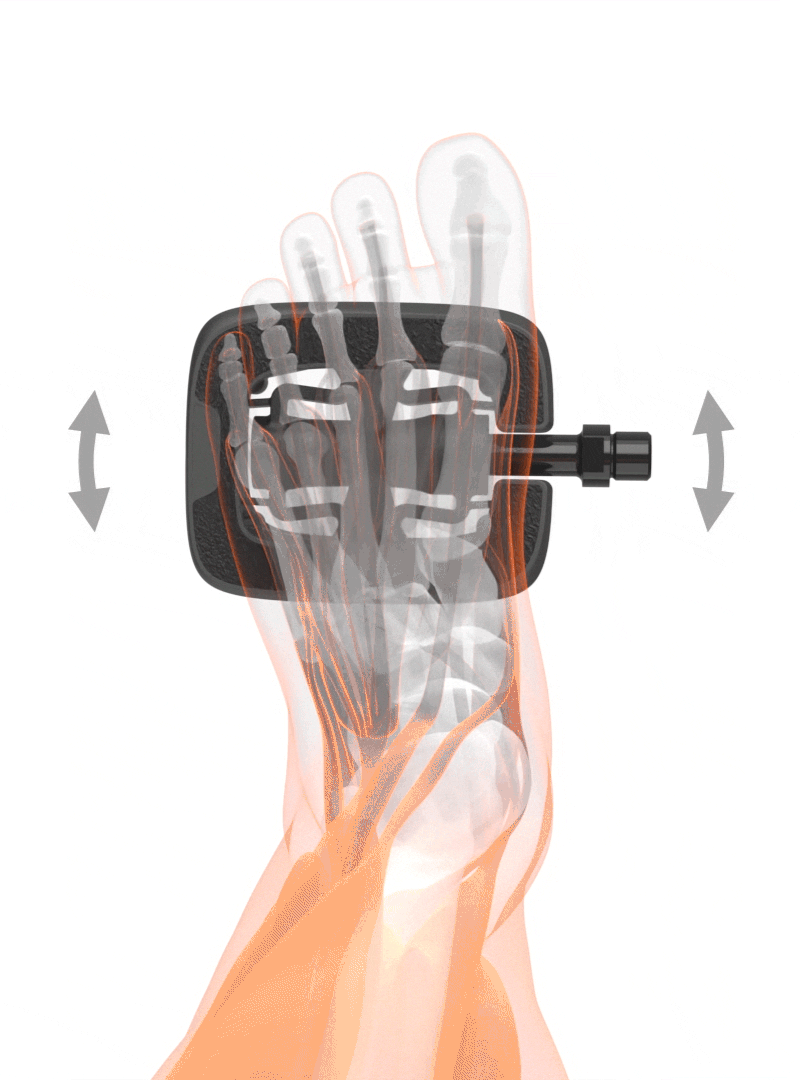
Knee pain due to restricted joint movement
Cause - restricted joint movement
Through a static position on the pedal.
SQlab solution
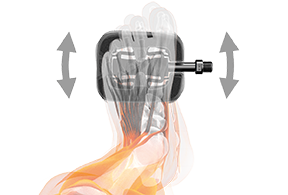
Pedals with a lateral freedom of movement for a physiologically correct pedaling motion.
Freedom starts at the foot
What is the advantage of this freedom of movement?
+ Natural movement of the foot
+ Foot position is determined by the knee
+ Knee joint is relieved
The position of the foot on the pedal has a direct influence on the rotation axis in the knee joint. An unnaturally twisted position of the feet on the pedal also causes a rotation of the lower leg and changes the natural joint movement in the knee. The one-sided load can lead to pain and increased wear of the joint.



.contact)